Are you ready to find 'ethanol production thesis'? You can find all the material on this web page.
Thesis Bioethanol Production Connected Ethanol is produced by fermentation of sugars from sugar cane or sugar beetroot, and indirectly from more complex carbohydrates such as amylum from corn, wheat berry, potatoes or casava.
Table of contents
- Ethanol production thesis in 2021
- Production of ethanol from starch pdf
- Corn ethanol energy balance
- Ethanol production process pdf
- Corn ethanol production process
- Production of ethanol from sugarcane flowchart
- Ethanol production from sugarcane project report
- Ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse pdf
Ethanol production thesis in 2021
 This picture demonstrates ethanol production thesis.
This picture demonstrates ethanol production thesis.
Production of ethanol from starch pdf
 This picture representes Production of ethanol from starch pdf.
This picture representes Production of ethanol from starch pdf.
Corn ethanol energy balance
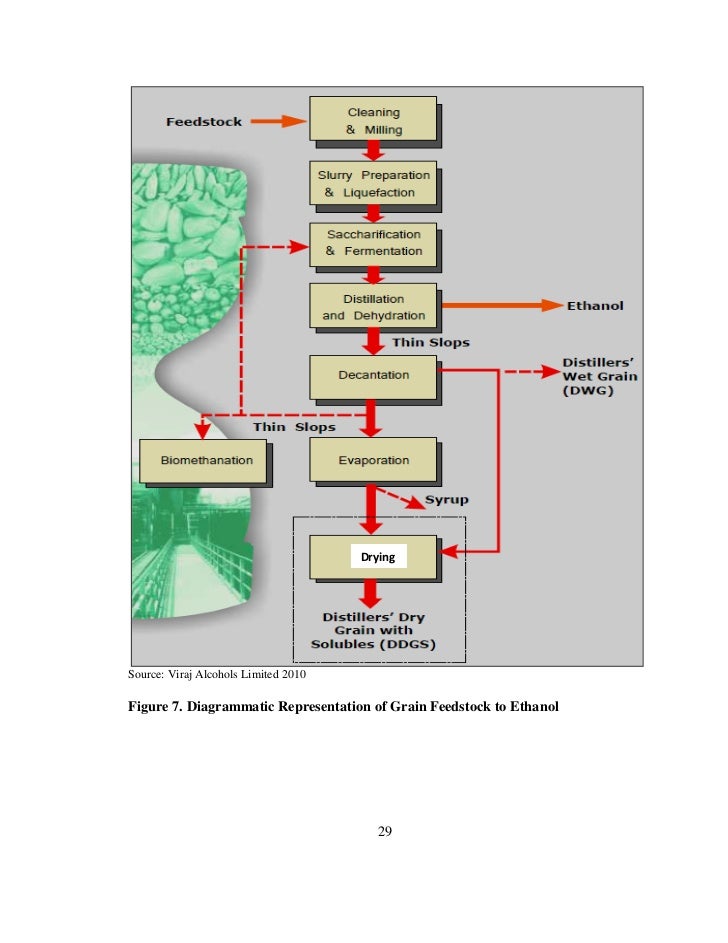 This image shows Corn ethanol energy balance.
This image shows Corn ethanol energy balance.
Ethanol production process pdf
 This picture demonstrates Ethanol production process pdf.
This picture demonstrates Ethanol production process pdf.
Corn ethanol production process
 This picture illustrates Corn ethanol production process.
This picture illustrates Corn ethanol production process.
Production of ethanol from sugarcane flowchart
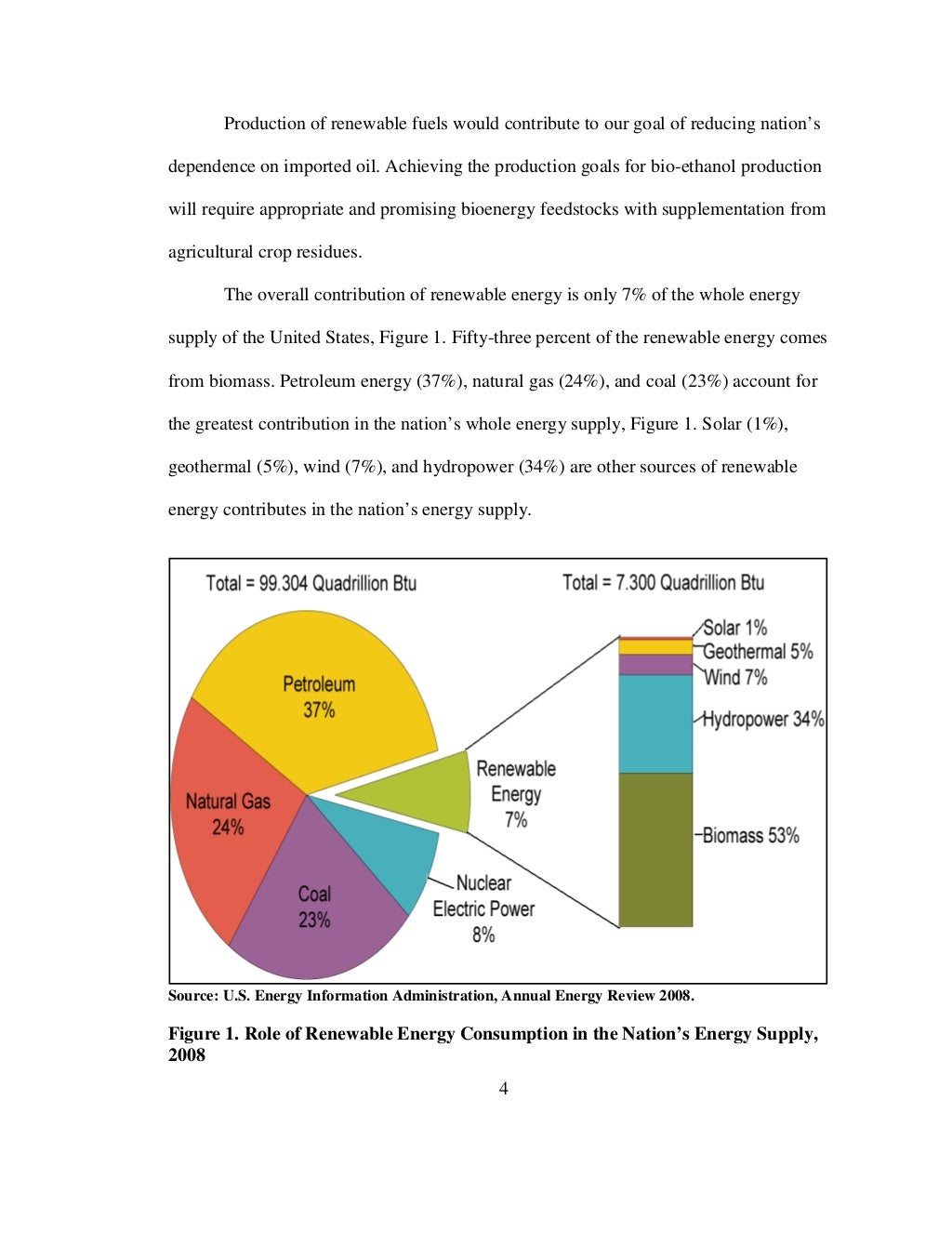 This image representes Production of ethanol from sugarcane flowchart.
This image representes Production of ethanol from sugarcane flowchart.
Ethanol production from sugarcane project report
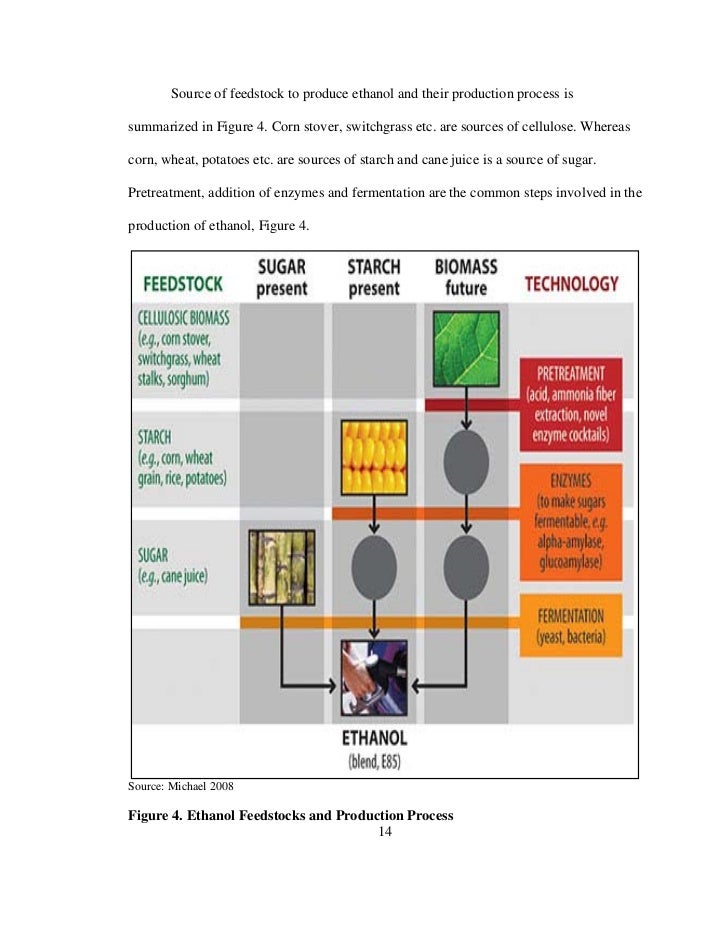 This image shows Ethanol production from sugarcane project report.
This image shows Ethanol production from sugarcane project report.
Ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse pdf
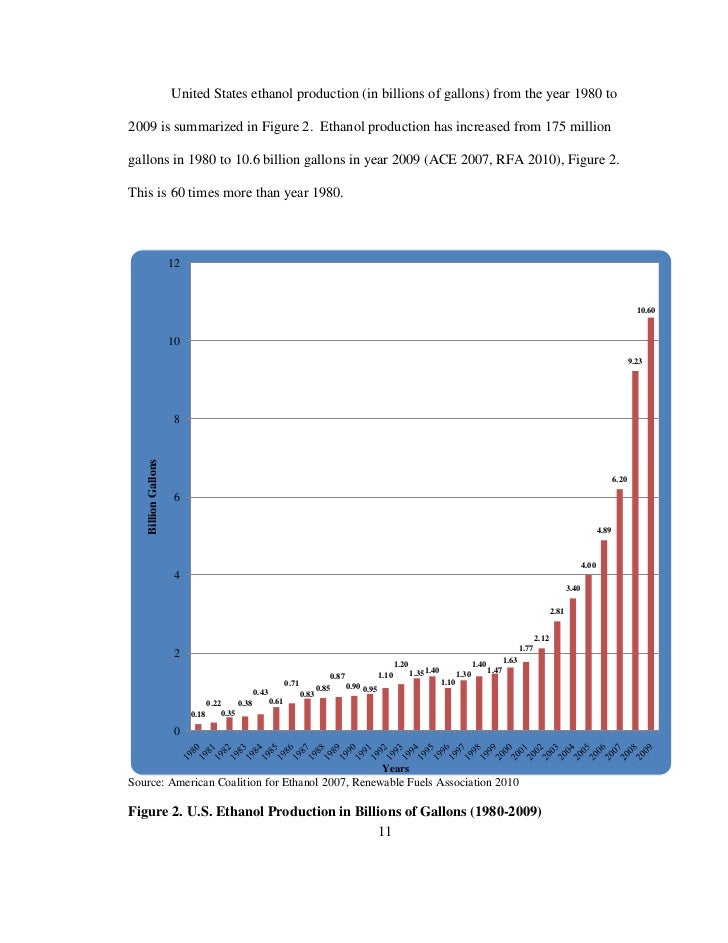 This image shows Ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse pdf.
This image shows Ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse pdf.
Is there a market for waste based bio-ethanol?
Waste-based bio-ethanol: Estimating production, demand and turnover The market size for biofuels has largely de- pended on EU directives, which mandate min- imum levels of consumption to be attained by each member State.
How are purification techniques used in the ethanol industry?
common purification technique utilized in the ethanol industry is rectification by further distillation. However, distillation has critical disadvantages including high cost and limited separation capacity. irradiation, oxidation of impurities by ozone, and adsorption of impurities by activated carbon or zeolite.
How much corn is used to make ethanol?
Ethanol is a renewable source made mostly from corn starch, and nearly 97 percent of gasoline contains ethanol in the USA. Corn for producing ethanol increased its production from 3 billion bushels in 2007 to over 5 billion bushels, which is almost 32 percent of total corn consumption in 2015.
How is bio-ethanol produced from residues and wastes?
To address these concerns, bio-ethanol can be derived from a large variety of residue and waste streams – either by capturing sugar or starch rich waste streams or by using waste fractions of crops (so-called ligno-cellulosic biomass). The for- mer is significantly easier to ferment and has more mature required processing technologies.
Last Update: Oct 2021